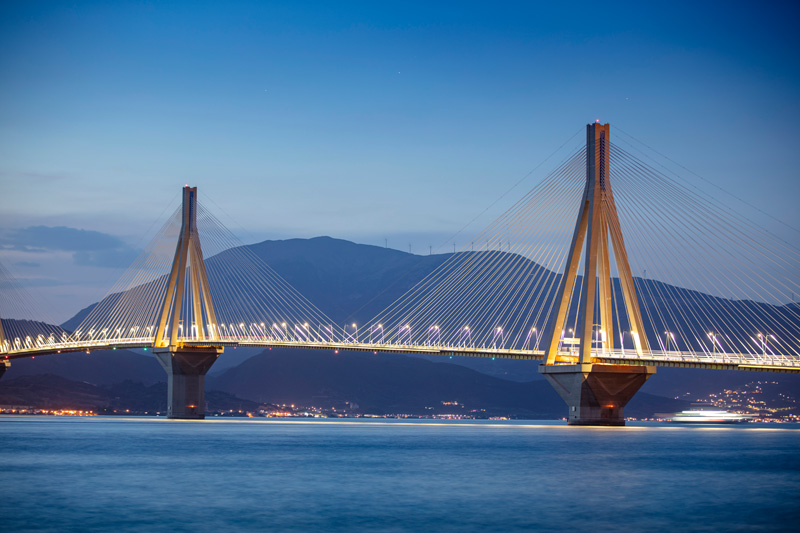
The Roots of the Bridge The anchorages of the Messina Strait Bridge are monumental structures, largely invisible to most, yet crucial for the balance of the entire work. Located on both shores, their task is to secure the main cables to the ground, countering the enormous tensile forces generated by the weight of the suspended span, traffic, and environmental stresses. True hidden giants, the anchorages represent the “roots” of the bridge.
The Anchorages of the Messina Bridge
Messina Bridge
The four anchorages of the Messina Strait Bridge constitute a fundamental component of the entire structural system, often less visible than the towers or the suspended span, but essential for the overall stability of the work. They consist of enormous, carefully designed reinforced concrete blocks, whose function is to secure the main cables to the ground, preventing them from sliding or deforming under the action of loads. Thanks to these monumental masses, the load-bearing cables can remain constantly under tension, ensuring the proper support of the road and railway deck.
The role of the anchorages is comparable to that of horizontal foundations: while the towers transfer loads downwards, the anchorages counteract the longitudinal forces exerted by the cables, absorbing the thrusts and ensuring that the static equilibrium of the entire bridge is maintained even in the presence of intense traffic, thermal variations, wind, or seismic stresses. Without these devices, the imposing suspended structure could not exist: every oscillation of the deck or tension generated by the passage of vehicles would find in the anchor blocks the necessary point of resistance to preserve the integrity of the span.
These four elements, strategically located on both shores of the Strait, are designed to integrate with the ground and exploit its natural bearing capacity. Geological analyses have identified areas where the bedrock guarantees maximum anchorage, reducing the risk of settlement. Inside the enormous plinths, inspection tunnels and technical rooms allow maintenance personnel to safely monitor cable tensions, check the condition of metal plates, and schedule any preventive maintenance interventions.
HIGHLIGHT
Messina Bridge
IN DETAIL
Messina Bridge
Structure and Dimensions
Messina Bridge
The four anchorages will be distributed on the two shores of the Strait, in areas carefully selected for their geological stability. Each anchorage consists of a monolithic reinforced concrete structure of monumental dimensions, capable of housing the saddles and devices that connect the main cables to the ground. The overall mass is designed to oppose the cable tension, which can reach hundreds of thousands of tonnes.
The internal structure of each anchorage includes service tunnels and inspection chambers that allow technicians to safely check the condition of the elements, perform tension checks, and plan any maintenance. The connections with the cables are made with special plates and anchor blocks of high-strength steel, designed to ensure perfect adhesion and uniform stress distribution.
Foundations and Geotechnics
Messina Bridge
The design of the anchorages required in-depth geological and geotechnical studies, necessary to understand the characteristics of the ground and ensure the stability of the works. The foundations are built on compact rock substrates, capable of withstanding the horizontal thrusts exerted by the cables. Where necessary, micro-piles or steel bars are used to increase the bearing capacity and improve the interaction between the concrete block and the surrounding ground.
Particular attention has been paid to protection from erosion and the management of surface water, in order to avoid instability phenomena or infiltrations that could compromise the efficiency of the anchorage in the long term.

Materials and Technologies
Messina Bridge
The anchorages are made with high-performance concretes, designed to resist mechanical actions and aggressive agents typical of a marine environment. Inside, plates and bolting made of high-strength steel guarantee the perfect hold of the load-bearing cables. The spaces intended for inspection are equipped with lighting, ventilation systems, and sensors that constantly monitor the state of the connections and any micro-deformations.
The technology of “rock anchoring” – the insertion of bars or strands deep into the substrate – is used where the ground allows it, further increasing the overall safety. All components are designed to resist corrosion, with protective coatings and drainage systems to limit moisture accumulation.

Dynamic Function and Maintenance
Messina Bridge
The anchorages are not static elements: they must adapt to the movements of the bridge caused by thermal variations, wind, or earthquakes. For this reason, the connection devices include joints and adjustment systems that allow small, controlled displacements, avoiding stress concentrations.
Maintenance is planned on multiple levels: periodic visual inspections, instrumental checks on the cables, and verification of structural parameters via sensors connected to the continuous monitoring system of the entire bridge. This strategy allows for the early detection of any anomalies and the scheduling of targeted interventions without interfering with the normal operation of the infrastructure.

Symbolic and Environmental Value
Messina Bridge
Although hidden from view compared to the towers and the span, the anchorages have strong symbolic significance: they represent the “roots” of the bridge, the material link between the work and the two regions it connects. Their construction is carried out with particular attention to the landscape context, integrating the works with green barriers, screens, and environmental compensation interventions to reduce visual impact and enhance the surrounding areas.

Data Related to the Messina Bridge Anchor Blocks
Messina Bridge
| Parameter | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Function | Secure the main cables to the ground, absorbing tensile forces and maintaining the suspended deck under tension. |
| Location | On both shores of the Strait, in areas selected for geological stability and ease of access. |
| Structure | Four monolithic reinforced concrete blocks, with internal tunnels for inspections and maintenance. |
| Estimated Dimensions | Large volume footings (tens of thousands of m³), designed to counteract tensions up to hundreds of thousands of tonnes. |
| Materials | High-performance concretes and high-strength steels with anti-corrosion treatments. |
| Foundations | Support on rock substrates; use of micro-piles or steel bars to increase bearing capacity. |
| Monitoring Systems | Sensors to measure tensions and micro-displacements; internal tunnels for visual checks and scheduled maintenance. |
| Environmental Protection | Landscape screens, green barriers, and compensation works to integrate the blocks into the natural context. |
| Symbolic Value | They represent the “roots” of the bridge, materially linking Sicily and Calabria through a work of engineering and landscape. |






