The Value of Suspenders The suspension cables, or suspenders, are an essential component of the structural system of suspension bridges. They connect the deck to the main cables, transferring vertical loads to them and contributing to the stability of the entire span. Despite having much smaller dimensions compared to the main cables, the suspenders play a crucial role: they distribute the weight of the entire deck, trains, and vehicles in transit uniformly along the entire suspended span.
The Suspension Cables of the Messina Strait Bridge
Messina Bridge
The suspension cables, also known as suspenders, constitute an essential component of the structural system of the Messina Strait Bridge. They connect the deck to the main cables, continuously transferring vertical loads and contributing to the stability of the entire span. Although they have much smaller dimensions compared to the large load-bearing cables, the suspenders play a crucial role: they distribute the weight of the roadway, trains, and vehicles in transit, ensuring that stresses are evenly distributed along the entire suspended span.
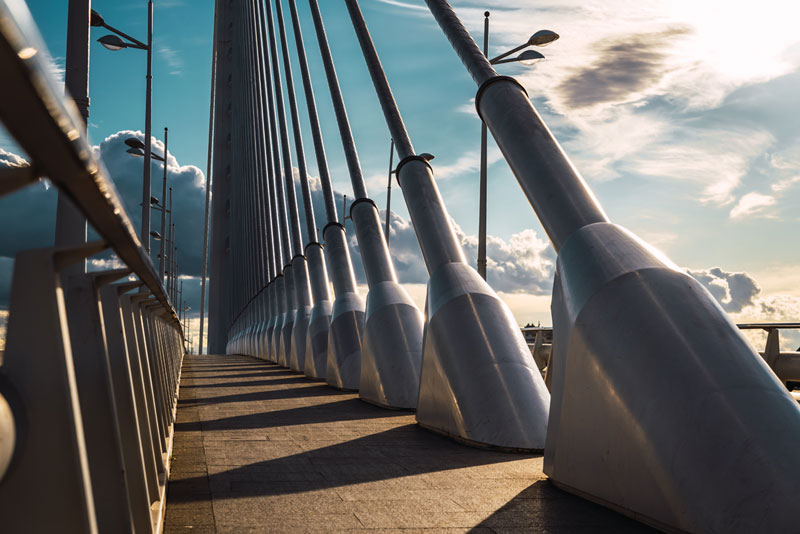
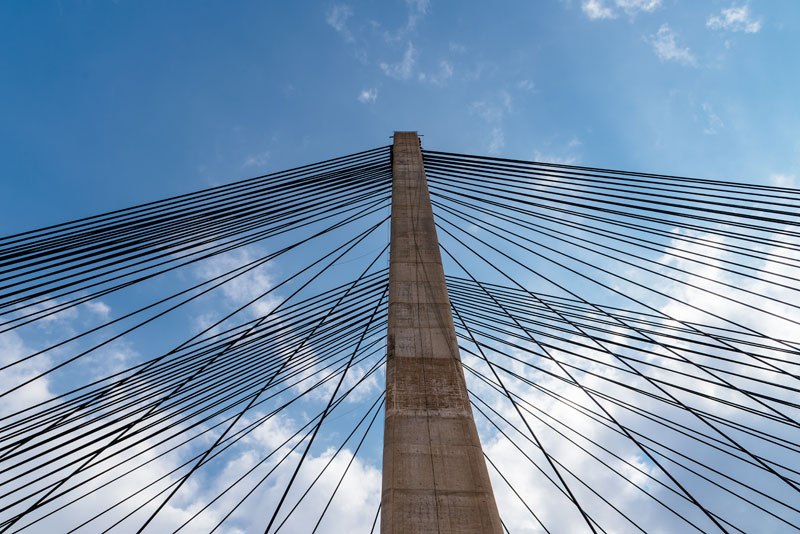
The suspenders are made of vertical high-strength steel ropes, designed to support significant loads despite their smaller diameter compared to the main cables. They are fixed via steel collars placed at regular intervals of 30 meters, which connect each pair of main cables. This system allows for the effective distribution of both static and dynamic forces generated by road and rail traffic and by environmental stresses such as wind or earthquakes. Thanks to this function, the suspenders ensure a balanced distribution of tensions, crucially safeguarding the structural integrity of the entire span.
In addition to transmitting vertical loads, the suspenders also help maintain the geometry of the structure, preventing excessive deformations of the deck that could compromise the safety and functionality of the bridge. Each suspender works in synergy with its neighbors, forming an integrated system that supports the deck along its entire 3,300-meter suspended length. The high-strength material used, together with protective treatments against corrosion and weather, ensures long life and reduced need for maintenance over time, fundamental elements for a structure of this size and importance.
Although thinner and less prominent than the colossal main cables, the suspenders perform an indispensable structural function in the Messina Bridge. They ensure the uniform transmission of loads across the entire suspended span, maintaining the static and dynamic equilibrium of the bridge and contributing significantly to its safety and longevity over time. Without their contribution, the main cables could not effectively support the deck and the traffic in transit, compromising the functionality and stability of the entire infrastructure work.
HIGHLIGHT
Messina Bridge
IN DETAIL
Messina Bridge
Structure and Materials
Messina Bridge
Each suspension cable consists of strands or bars of high-strength steel, protected by anti-corrosion sheaths. Their diameter varies depending on the position along the bridge: those located at the center of the span, where the loads are greatest, are more robust, while those near the towers can be thinner. The use of micro-alloyed steels and special coatings ensures long durability even in an aggressive environment like that of the Strait, characterized by salt spray, wind, and thermal variations.
Layout and Function
Messina Bridge
The suspenders are arranged at regular intervals along the main cables, creating a dense and orderly network that supports the road and railway deck. Their function is to transform the vertical weight of the span and traffic into distributed forces, which are then transmitted to the main cables and from there to the towers and anchorages. This configuration allows the bridge to remain stable even under conditions of intense traffic or strong wind, reducing deformations and oscillations.

Installation Techniques
Messina Bridge
The installation of the suspension cables requires delicate operational phases. After the completion of the main cables, the suspenders are fixed using clamps or specific devices, then connected to the deck with high-strength plates and bolts. Each element undergoes careful tension calibration to ensure that the forces are distributed homogeneously and that the bridge does not exhibit sags or irregularities. During these operations, precision instruments and mobile platforms that run along the cables are used, allowing technicians to work safely.

Maintenance and Monitoring
Messina Bridge
As with other vital parts of the bridge, the suspenders will also be subject to a continuous Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) system. Sensors installed on some sample elements will record variations in load, vibrations, and temperature, allowing for the detection of any anomalies and the planning of targeted interventions. Periodic inspections will include visual checks, dynamic tests, and verification of anti-corrosion protection, with the aim of maintaining a constant level of safety and performance over time.

Symbolic Value
Messina Bridge
In addition to their technical function, the suspension cables contribute to the overall elegance of the bridge. Their regular arrangement creates a visual rhythm that guides the eye along the span, integrating engineering with the landscape of the Strait. This subtle yet resilient texture is a tangible sign of how technology can dialogue with nature: seemingly lightweight threads that, in reality, support one of Europe’s most ambitious infrastructures.

Data Related to the Messina Bridge Suspension Cables
Messina Bridge
| Parameter | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Vertical cables connecting the deck to the main cables, transferring loads to the supporting system. |
| Estimated Number | Over 500 suspenders distributed along the suspended span (indicative value, to be confirmed in executive phase). |
| Installation Spacing | Approximately every 10–12 m along the main cables, variable based on load zones. |
| Indicative Diameter | From 50 to 120 mm, larger in the central zone of the span, smaller near the towers. |
| Materials | High-strength steel with zinc coating; anti-corrosion protective sheaths. |
| Structural Function | Distribute the weight of roadway, tracks, and traffic, transmitting loads to the main cables and towers. |
| Installation | Fixing with clamps on main cables and plates on the deck; calibrated tensioning with precision instruments. |
| Protection | Anti-corrosion coatings and drainage systems to prevent stagnation and oxidation. |
| Monitoring | Tension and vibration sensors connected to the SHM system; periodic inspections and dynamic tests. |
| Aesthetic Role | Contribute to the visual rhythm of the span, creating a harmonious effect that enhances the bridge’s profile. |
| Note: Data and dimensions are indicative, subject to refinement during the executive design phase. | |







